singularity
- https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo-en/
-
https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo-en/ii.-data-structure/framework-and-thoughts-about-learning-data-structure-and-algorithm
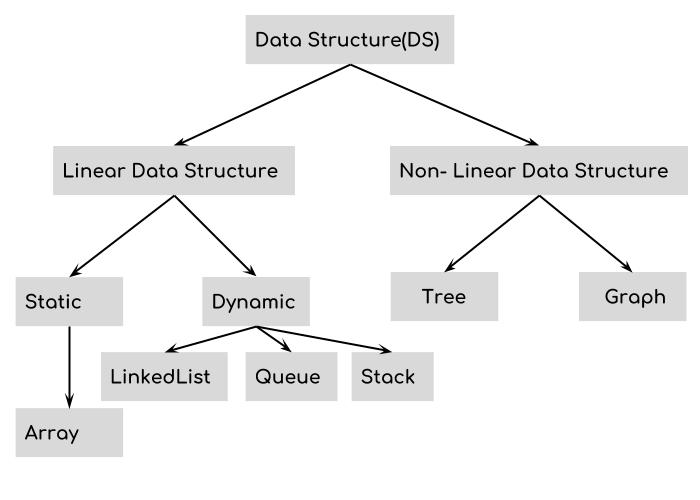
1.Storage mode of data structure
2️⃣ There are only two ways to store data structure:
1. array (sequential storage) 2. linked list (linked storage)。
- Hash table, stack, queue, heap, tree, graph and so on belong to the 「superstructure」, while arrays and lists are the 「structural basis」
-
For example, 「queue」 and 「stack」 data structures can be implemented with both linked lists and arrays. Graph can be implemented with both linked lists and arrays.
Using array to realize, we need to deal with the problem of expanding and shrinking capacity; using linked list to realize, there is no such problem, but more memory space is needed to store node pointers.
- Even you can invent your own data structures, but the underlying storage is nothing but arrays or linked lists.
if the array is to be expanded, it needs to reallocate a larger space, and then copy all the data, the time complexity O (n); and if you want to insert and delete in the middle of the array, you must move all the data behind each time to maintain the continuity, the time complexity O (n)
if you know the precursor and the hind drive of an element, the operation pointer can delete the element or insert a new element, with time complexity of O (1).
But because the storage space is not continuous, you can’t calculate the address of the corresponding element according to an index, so you can’t access it randomly; and because each element must store a pointer to the location of the front and back elements, it will consume relatively more storage space.
2.Basic operations of data structure : traversal + crud
```
// array traversal
void traverse(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// iteratively visit arr[i]
}
}
// linked list traversal iterative
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
}
void traverse(ListNode head) {
for (ListNode p = head; p != null; p = p.next) {
// iteratively p.val
}
}
//linked list traversal recursive
void traverse(ListNode head) {
// recusively head.val
traverse(head.next)
}
//binary tree traversal
/* Basic node of the binary tree */
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left, right;
}
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root.left)
traverse(root.right)
}
//n-tree traversal
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode[] children;
}
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
for (TreeNode child : root.children)
traverse(child)
}
```
- N-tree traversal can be extended to graph traversal, because graph is a combination of several n-tree. Do you think a circle can appear in a graph? This is very easy to do. Just mark it visited with a Boolean array.
3.Guidelines of Algorithm Exercises
it should be clear that data structure is a tool, and algorithm is a method to solve specific problems through appropriate tools. That is to say, before learning algorithms, at least we need to understand the common data structures and their characteristics and defects.
Do binary tree exercises first! Do binary tree exercises first! Do binary tree exercises first! Because binary tree exercises are the easiest to train framework thinking, and most of the algorithm skills are essentially tree traversal problems.
Don’t look down on following lines of broken code, almost all the topics of binary trees are a set of this framework.